Understanding the recent npm malware attacks
What happened, why it matters, and how Sonatype protects you from npm-ecosystem malware
Two npm-ecosystem malware attacks, PhantomRaven (SonatypeID: sonatype-2025-004344) and IndonesianFoods (SonatypeID: sonatype-2025-004546), were recently identified. Both of these attacks are novel developments in malware sophistication and aggression. PhantomRaven abuses a feature of npm to hide dependencies from surface-level threat scanners while give attackers contextual control over payloads. IndonesianFoods, like the Shai-Hulud attack earlier this fall, is self-replicating, capable of publishing new, infected packages to npm automatically.
These new characteristics highlight the importance of proactive malware defense. Sonatype Repository Firewall draws provides real-time protection by automatically quarantining malicious components at the moment they would enter your environment. For more detailed information, see our documentation on how Sonatype identifies malware and review our blog posts on the PhantomRaven attack and IndonesianFoods attack.
What to do if your files have been compromised
Prerequisites
To take advantage of the remediation steps outlined below, customers must be on Nexus Repository Pro version 3.73.0 or higher. Customers must also have Sonatype Repository Firewall, and the IQ Server and Nexus Repository must be connected.
If a malicious component was downloaded before Repository Firewall was properly configured, you can use the following steps to find and remove it:
Using Nexus Repository:
Check for the Malware Banner on your repository dashboard (version 3.73.0 or higher), which indicates that a malicious component has been identified. Download a CSV list of components from the Malware Banner.
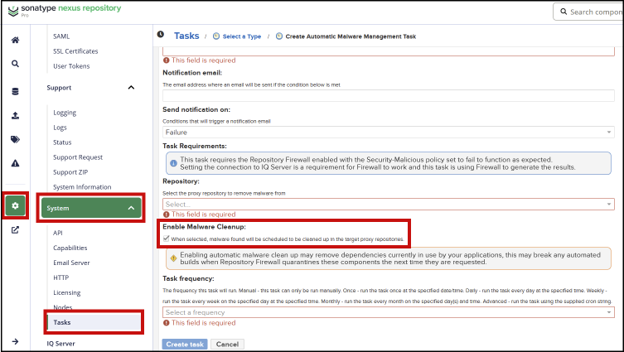
To remove the malicious components, run the Automatic Malware Management task on the affected proxy repositories (version 3.77.0 or higher). This task, when enabled with Enable Malware Cleanup, will automatically delete the malicious components from your repository. For details, including instructions for creating the task, refer to the Automatic Malware Management task documentation.
Using IQ Server:
Utilize Advanced Search in IQ Server to find any violations related to these specific attacks. For PhantomRaven, use the following search criteria:
vulnerabilityId:sonatype-2025-004344
And for IndonesianFoods, use the following search criteria:
vulnerabilityID:sonatype-2025-004546
To search both at the same time, separate the search criteria with “OR.”
vulnerabilityId:sonatype-2025-004344 OR vulnerabilityID:sonatype-2025-004546
If Advanced Search returns results, then a Lifecycle scan has identified these components in your codebase. Follow your internal incident response policy and aim to remove those packages from your builds and manifest files immediately.
For a comprehensive guide on the manual process of removing malware and handling the malware banner, please consult the Guide to Removing Malware.
Check now that your deployments of Nexus Repository and Repository Firewall were/are correctly configured to block malware
Open Repository Firewall and:
Confirm that all proxy repositories for the npm ecosystem have Audit and Quarantine enabled. Sort the list by Format to quickly identify npm proxy repositories.
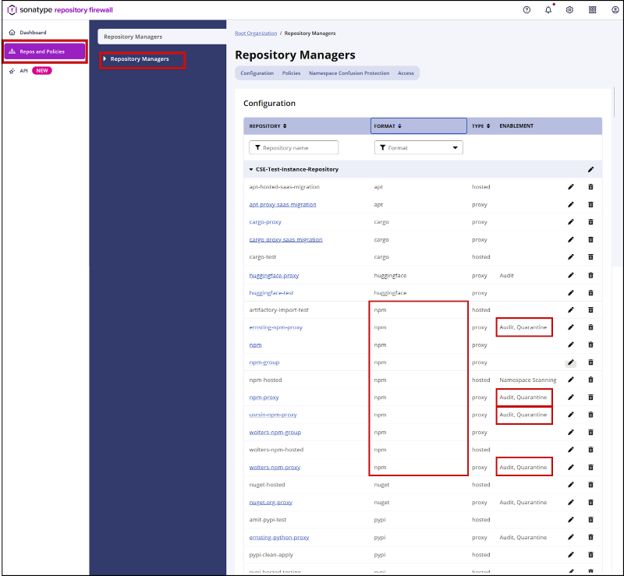
Read more: Audit and Quarantine documentation
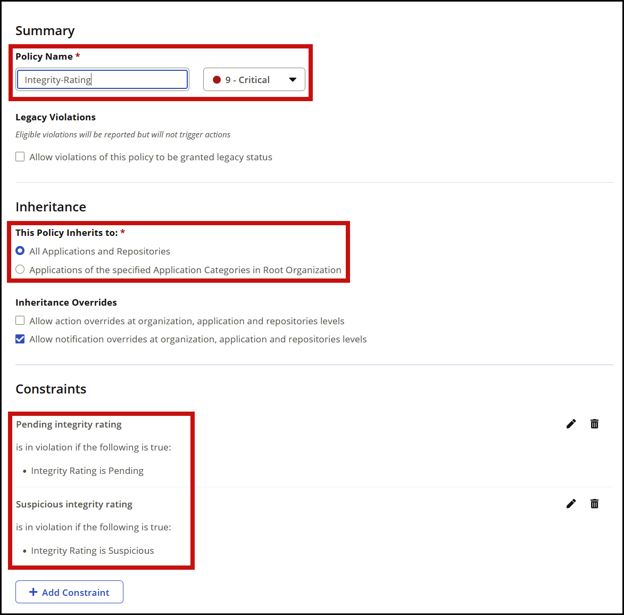
Confirm that your Integrity-Rating and Security-Malicious policies are configured correctly. Make sure they match these screenshots exactly, including the Policy Name field.
Integrity-Rating:
To understand the protection provided by the Release Integrity policy please see our Release Integrity documentation. Policy Compliant Component Selection should also be considered in conjunction with this policy to minimize impact from the latest suspicious packages.
Security-Malicious:
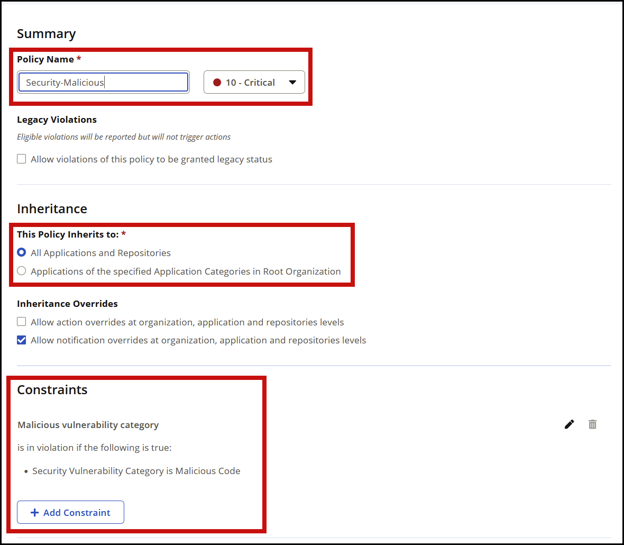
Confirm that both of these policies are set to "Fail" at the proxy stage.
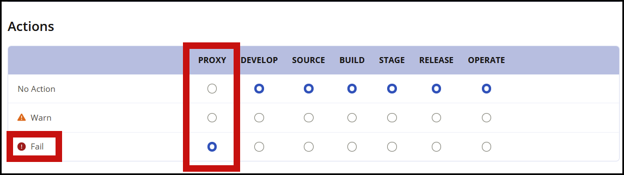
Confirm that both of these policies are set to "Fail" at the proxy stage.
If all of these things are confirmed, congratulations: You're protected against these npm malware attacks and the 850,000+ other malicious packages Sonatype has cataloged!
Demo: Configuring Nexus Repository and Repository Firewall
The interactive demo below walks you through configuring the Automatic Malware Management task in Nexus Repository and the Integrity-Rating and Security-Malicious policies in Repository Firewall. Select the Next button below to navigate through the interactive demo:
Next Steps
Malware attacks are more frequent, more sophisticated, and more dangerous than ever. Maximize your protection against future malware attacks by doing the following:
Review the Integrity-Rating and Security-Malicious policies on a regular cadence and ensure they're set to "Fail" at the Proxy stage. If you're also a Sonatype Lifecycle customer, it's wise to set them to "Fail" at every stage. Remember – there's never a legitimate reason for malware to be in your development ecosystem.
Eliminate development disruption caused by the Integrity-Rating policy by also configuring Policy Compliant Component Selection.
Consider setting the Component-Unknown policy to also fail at the proxy stage. This protects you from malware that Sonatype hasn’t yet ingested or evaluated.
Create an Audit and Quarantine capability for every new proxy repository.
Enable Automatic Quarantine Release so that components are released from quarantine automatically if new data confirms they're safe. This avoids developer friction and minimizes "false positives."
If you're a Sonatype Lifecycle or Sonatype SBOM Manager customer, turn on Continuous Monitoring. This will alert stakeholders if malware appears in your apps unexpectedly.
Educate developers on the importance of routing component requests through Nexus Repository. All requests for open-source components, regardless of ecosystem or package manager, should go through Nexus Repository.
For additional protection, integrate Repository Firewall with Zscaler to block downloads of known malware even when developers bypass Nexus Repository.