npm audit
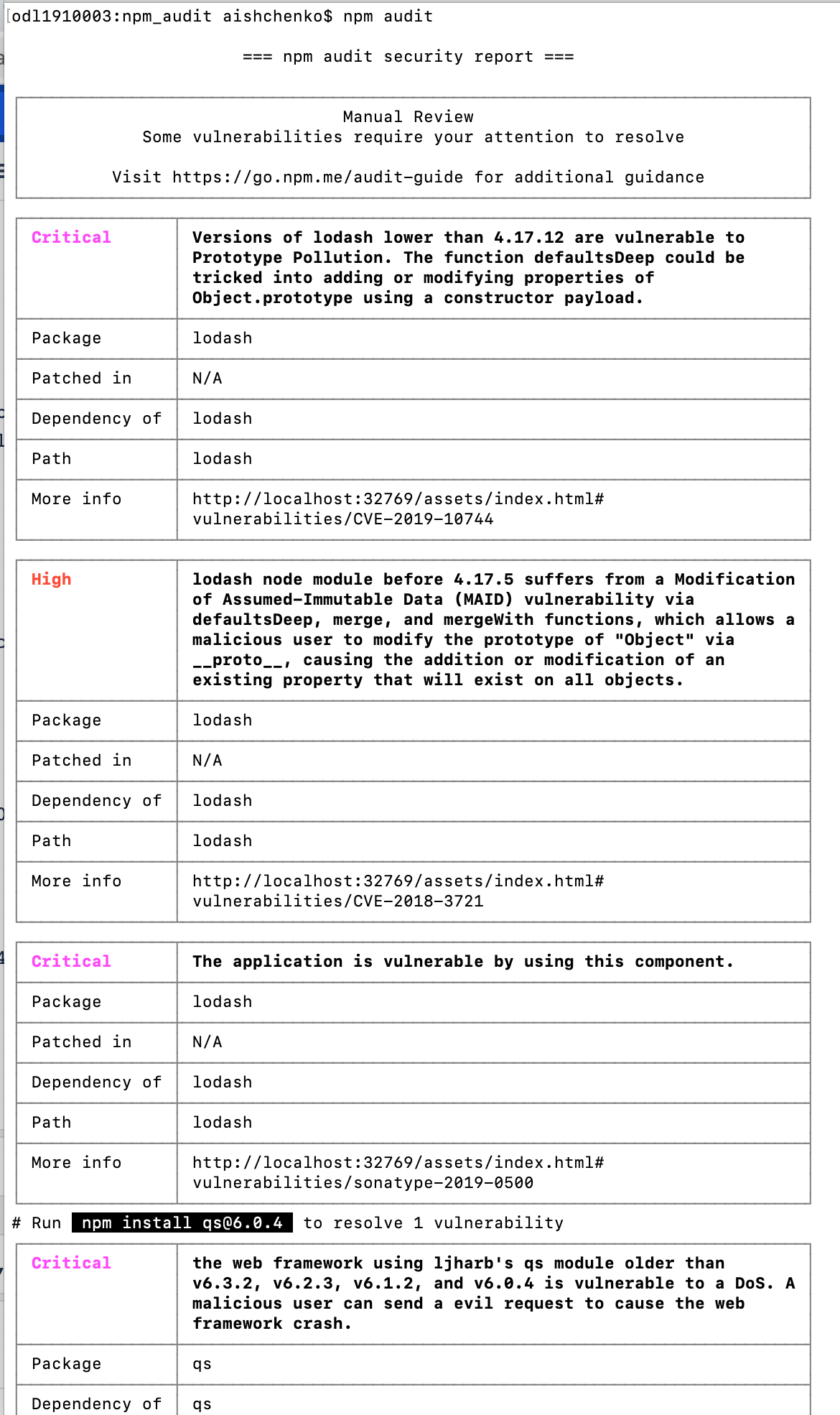
The npm audit command submits a list of the dependencies from your project and returns a report of security violations. The report includes instructions on how you could remediate the issues.
Nexus Repository may be configured to use Sonatype Repository Firewall as a data source for npm audit to return results that align with your open-source governance policies.
Requires a license for Sonatype Repository Firewall. Configure the Repository Firewall to audit your npm proxy repositories.
Configure your npm project within Nexus Repository to use the
npm auditcommand from the Repository Firewall.See Configuring npm
npm auditis supported with proxy and group repositories.Use
npm audit fixto automatically remediate vulnerable dependencies.
Setup
You have the option to evaluate npm packages using the policies configured for a specific application or the set used to cover the entire repository.
Update the local .npmrc file (requires npm 6) Add the following line while including the application ID:
headers[]="app_id:<application_id>"
Without the application ID Not including the application ID returns the results using the root organization policies. These reports do not include which violation would fail a build and are not scoped to the application's license policies.
Troubleshooting
Reset the audit cache Audit information is locally cached for 12 hours. Invalidating the cache at the repository level clears the audit cache.
Increase the npm timout npm v6.14.4 limits requests to 30 seconds while most evaluations take just under a few minutes to finish. Add the timeout flag to increase the amount of time to fetch the results.
npm audit --timeout=300000
Force update the lock file If you don't get the application ID using the script try purging the cache with the following commands:
npm cache clean --force npm clean install
Error message example You will receive the following message if the configuration is incomplete or incorrect: