Proxying RHEL Yum Repositories
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is subscription-based and communicates with remote Yum repositories over HTTPS. To set up a proxy in Nexus Repository for this scenario, Nexus Repository must trust the remote certificate and also authenticate when requesting packages from the remote server.
The following demonstrates how to configure Nexus Repository for SSL communication with RHEL remote Yum repositories.
Prerequisites
You have a RHEL subscription (See the RHEL site for details).
You have downloaded SSL certificates for your Red Hat subscription.
The RHEL Subscription SSL certificate may expire or become invalid by RHEL systems. Manual validation is required to obtain a new certificate and redo the below steps before the certificate expires and avoid unexpected downtime.
You have imported your certificates onto your RHEL instance using the subscription-manager command-line tool that comes with RHEL.
Ensure you have the Java keytool installed on your RHEL instance. The Java keytool is part of the JDK; you can install JDK 8 to obtain it.
Proxying Yum Repositories on RHEL
We are using a RHEL7 docker image for the following demonstration.
registry.redhat.io/rhel7:latest
On your RHEL instance, confirm that the certificate and associated private key files are in your entitlement directory.
/etc/pki/entitlement
When importing the RHEL subscription certificate, the RHEL subscription-manager command-line utility puts the certificate and associated private key files in this directory by default.
In your RHEL terminal, run the command below (you should specify your RHEL entitlement certificate and key as appropriate).
openssl pkcs12 -export -in /etc/pki/entitlement/4616881636184323465.pem -inkey /etc/pki/entitlement/4616881636184323465-key.pem -name certificate_and_key -out certificate_and_key.p12 -passout pass:password
In your RHEL terminal, run the command below. After running the command, you should have a file called
keystore.p12in your current directory.keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore certificate_and_key.p12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -srcstorepass password -deststorepass password -destkeystore keystore.p12 -deststoretype PKCS12
If you have an existing key store file (i.e., not a trust store), then you need to import the contents of the
keystore.p12file created in step 3 above into your existing key store file.On your Nexus server, do the following:
Make a backup of your existing key store file.
Run the commands below:
keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore existing_keystore.p12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -srcstorepass existing_keystore_password -deststorepass password -destkeystore new_combined_keystore.p12 -deststoretype PKCS12 keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keystore.p12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -srcstorepass password -deststorepass password -destkeystore new_combined_keystore.p12 -deststoretype PKCS12
On your RHEL server, create a
nexus.repofile in/etc/yum.repos.ddirectory similar to the following:[nexus] name = Nexus Repository enabled = 1 gpgcheck = 1 baseurl = http://ipaddress:port/repository/rhel-proxy/$releasever/$basearch/os ui_repoid_vars = releasever basearch gpgkey = file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release priority=1
Note
With
gpgcheckto 1 (i.e., enabled), provide the location of thegpgkey, replacing the value above.On your Nexus server, put the following Java system properties in your
$app-dir/bin/nexus.vmoptionsfile, or if the properties already exist in that file, update to reference the new key store. You'll need to make thekeystore.p12 or new_combined_keystore.p12file created above is accessible to Nexus Repository on the machine running it.-Djavax.net.ssl.keyStore=<path to keystore file> -Djavax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword=<keystore password specified earlier for the keytool command>
After making changes to
$app-dir/bin/nexus.vmoptionsor the keystore it references, you must restart Nexus Repository so that it can pick up the change.In Nexus Repository web UI, set up a yum proxy repository.
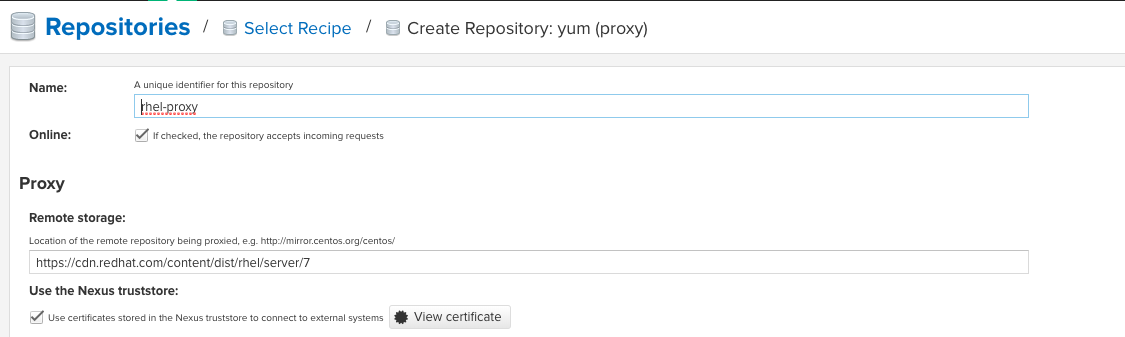
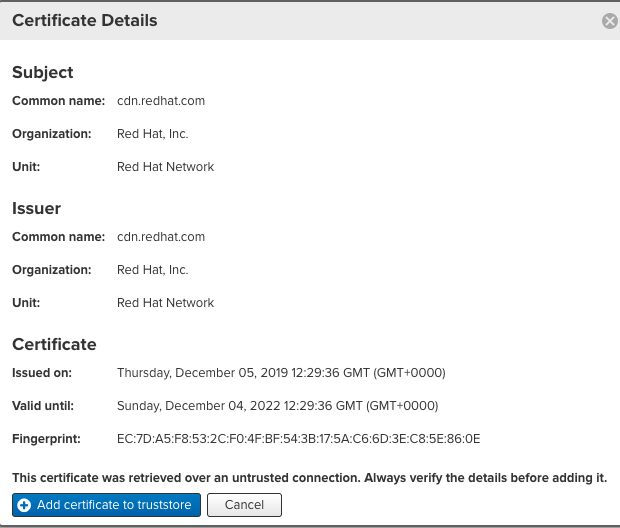
Click on the View Certificate button; when the Certificate Details pop-up displays, select Add a certificate to trust store.
If you install a package with yum, you should see in the RHEL terminal that it's downloading packages from the Nexus repository.
Note
If you’re using Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9, review the following section about SHA-1 deprecation before connecting to your Yum proxy repository.
SHA-1 Deprecation in RHEL 9
RHEL 9 deprecates the use of SHA-1 digest algorithm. Under RHEL 9’s default cryptographic policy, SHA-1 is disabled for both certificate signatures and package signature verification.
This change affects environments where remote Yum repositories or certificate chains use SHA-1 signatures — for example, older or third-party repositories. When such a repository is proxied through Sonatype Nexus Repository, RHEL 9 clients may fail to connect or verify packages.
Recommended Action
To ensure secure and reliable communication between Nexus Repository and RHEL 9 clients:
Obtain updated root certificates from Red Hat.
Install a new version of the Entitlement Master CA root certificate that is signed with a modern, supported algorithm.
Update the system’s trust store to include the stronger certificate. For more details, refer Configuring SSL.
Note
RHEL 9 provides a compatibility mechanism to temporarily re-enable SHA-1 support by using the DEFAULT:SHA1 sub policy. This workaround allows backward compatibility but is not recommended, as it reduces the system’s overall cryptographic security.
Sonatype advises to use this workaround only under the guidance of your IT or security teams. For more details, see the Sonatype article on temporarily enabling SHA-1.
Proxying Yum Repositories on RHEL 8+ with an AWS example
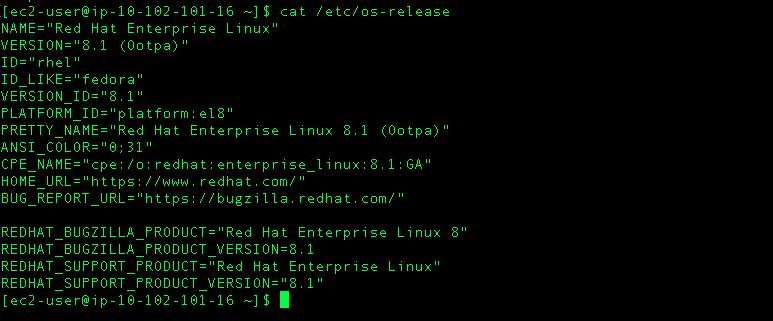
AWS RHEL 8 EC2 instance on which Yum will be proxied:
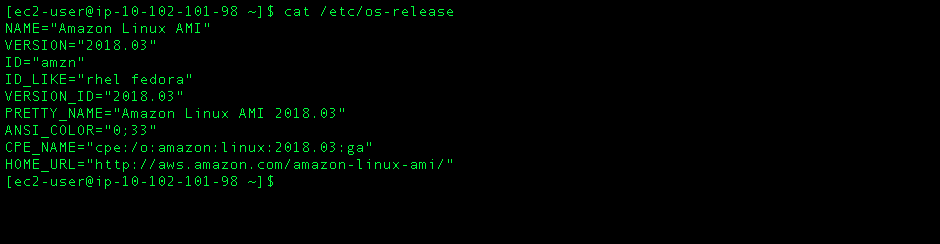
AWS Amazon Linux EC2 instance running Nexus Repository:
Follow the instructions in the Proxying Yum Repositories on RHEL with the following exceptions since the EC2 instance is running RHEL8.
The
nexus.repofile in/etc/yum.repos.ddirectory should be similar to the following:[nexus_baseos] name = Nexus Repository Baseos enabled = 1 gpgcheck = 1 baseurl = http://ipaddress:port/repository/rhel-proxy/$releasever/$basearch/baseos/os ui_repoid_vars = releasever basearch gpgkey = file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release priority=1 [nexus_appstream] name = Nexus RHEL x86_64 AppStream Proxy (RPMs) enabled = 1 gpgcheck = 1 baseurl = http://ipaddress:port/repository/rhel-proxy/$releasever/$basearch/appstream/os ui_repoid_vars = releasever basearch gpgkey = file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release priority=1
With
gpgcheckset to "1" (i.e., enabled), provide the location of thegpgkeyby replacing the value we've shown in the example above.In the Nexus Repository web UI, when you set up your yum proxy repository as specified in the Proxying Yum Repositories on RHEL, you should instead specify the remote URL.
https://cdn.redhat.com/content/dist/rhel8
When you install packages with yum (e.g.,
sudo yum install httpd -y), the terminal shows that it's downloading packages from the 'nexus_baseos' and 'nexus_appstream' repositories set up earlier.