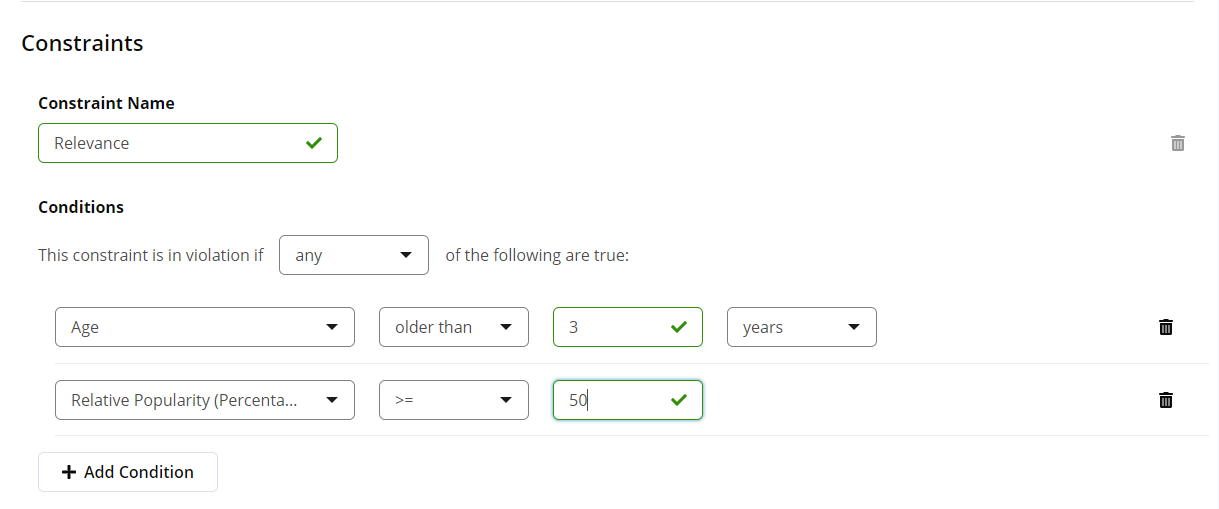
Policy Constraints
Policy constraints define the violating conditions to detect during a policy evaluation. A policy is considered in violation when any constraint of the policy evaluates to a true statement.
A policy must have at least one constraint and each constraint must have at least one condition.
Policy constraints may be configured to satisfy any or all of their conditions.
Policy constraints must have a unique name. These names are used as details for the policy violation.
 |
Policy Violation Conditions
Policy conditions determine how constraints are evaluated. Policies are in violation when any one of their constraints evaluates to TRUE.
ANY - When any condition is met, the constraint is evaluated to
TRUEand the policy will be in violation.ALL - When all conditions are met, the constraint is evaluated to
TRUEand the policy will be in violation. When any condition is not met, the constraint evaluates toFALSE.
Conditions for Unknown Components
A component is unknown when Sonatype does not have metadata for the component. Unknown components will only ever trigger the Match State, Proprietary, and Data Source conditions.
Policy Types
The policy type is automatically assigned, based on the conditions selected for the policy constraint. Policy Types are used for grouping and filtering policies.
The following priority is used to determine the policy type when the policy contains more than one of the specific conditions.
Security - contains any security conditions
License contains any license conditions
Quality contains age or popularity conditions
Other contains any other conditions from those above
Security Conditions
The following conditions are related to the security policy type.
Security Vulnerability Severity
This condition is associated with the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) of vulnerability and is commonly used as a bounding condition in combination with other conditions. The CVSS score is a number with a single digit with an escalating scale between 0.0 and 10.0.
For example, two conditions are used to determine the Security-High Policy , one set to greater than or equal to 7 and the other to less than 9. The constraint is set to ALL so that both conditions must be met.
Possible bounds:
equal (=), less than (<), less than or equal to (<=), greater than (>), greater than or equal to (>=)
Note
CVSS version 4 scores are used by default. In the case that a version 4 score is not available, the severity compared will be to the CVSS version 3 or 2 score.
Proprietary Name Conflict
Determine whether a component from a proxy repository has a name that matches the name of any proprietary component in a hosted.
This policy condition is only relevant to the Sonatype Repository Firewall.
Security Vulnerability Category
Verify if the security vulnerability category is or is not a specified category. If you've used the Component Information Panel, the vulnerability category values can be seen when viewing vulnerability information.
Data - The exploit involves the attacker sending a tainted request
Operational - The component is involved in the operation of the web server
Functional - Affects a specific piece of the component that isn't integral to the operation of the component
Configuration - Dependent on a specific configuration of the component implementation
Test Code - The vulnerability is in test code that is not required for production
Sample Code - The vulnerability is in an example included with the component
Privileged - The attacker needs to have elevated privilege levels to exploit
Malicious Code - The component has embedded malicious code
Other - Not covered in the above categories
Security Vulnerability Status
Verify if a component’s security vulnerability status is or is not one of the following values:
Open, Acknowledged, Not Applicable, Confirmed
Security Vulnerability CWE
Verify if a component’s security vulnerability CWE ID is or is not equal to a specified value.
Security Vulnerability Group
Verify if a component belongs to a specific vulnerability group. Custom vulnerability groups can be added using the Vulnerability Groups REST API - experimental.
Security Research Type
Verify if a component has undergone a fast-track or deep-dive research by the Sonatype Data Research team.
Verify if a component has undergone any one of the following research types:
Fast-Track
Sonatype's research process to make newly discovered vulnerabilities available to users within 24 hours of discovery. This process offers limited vulnerability data.
Deep-Dive
Sonatype's thorough research process to ensure accuracy of vulnerable version ranges with detailed source code analysis to provide detailed explanations and remediation recommendations, made available within 3 days of discovery.
Public Research
Vulnerabilities that are discovered via public research and do not undergo Sonatype's Fast-Track or Deep-Dive processes.
Vendor Research
Vulnerabilities discovered via third party vendors and do not undergo Sonatype's Fast-Track or Deep-Dive processes. These vulnerabilities are detected in Software Bill of Materials (SBOMs).
Security Vulnerability Custom Remediation
Verify if there is a Custom Vulnerability Remediation value or not for the vulnerability and evaluated application.
Security Vulnerability Detection Type
Verify if the vulnerability detection for the component follows any of the following processes:
Primary - The vulnerability data has been investigated by the researcher to explicitly implicate components referenced in the feed or as a result of their independent research.
Secondary - The component has been implicated by our automated systems because they share vulnerable code with components that were implicated by our primary systems.
AST - The vulnerability has been discovered as part of Application Security Testing (AST) and includes common issues such as code injection, authentication flaws, and data leakage.
Unshader: The vulnerability has been discovered by our Shaded Vulnerability Detection algorithm.
Other: The discovery of this vulnerability was not performed by us, but found in data sources external to Sonatype.
Security Vulnerability Custom CVSS
Verify if there is a custom vulnerability CVSS vector value for the vulnerability and evaluate application matching or not with a given regular expression.
License Conditions
The following conditions are related to the license policy type.
License Threat Group
Verify if a component’s license is or is not in a license threat group. The special value [unassigned] can be used to check whether a license has not been assigned to any of your license threat groups, i.e. represents an unknown risk.
License Threat Group Level
Verify if the threat level of a component’s license threat group matches a specified threat level value.
License Status
Verify if the status of a user-defined license is or is not one of the following values: Open, Acknowledged, Overridden, Selected, Confirmed.
License
Verify if the component license is or is not a specified license. If you’ve used the Component Information Panel to set a component’s license status to Overridden, then any licenses designated as Declared or Observed are ignored. If a component’s license status has not been overridden, then any occurrence (declared or observed) of the specified license is considered a match.
Quality Conditions
The following conditions are related to the quality policy type.
Relative Popularity (Percentage)
Verify if the relative popularity of a component’s version (as compared to other versions of the same component) is =, <, ⇐, >, or >= to a specified percentage value.
The Popularity of a component is calculated as a function of successful download counts from the Open Source Software repositories and package managers. As a baseline, the most popular version of the component will have 100% popularity. If all versions of component have the same popularity, roughly, then they would all have 100% popularity.
Age
Verify if a component is older than or younger than a specified value.
Hygiene Rating
Verify if the Hygiene Rating of a component is or is not one of the following:
Laggard
Exemplar
Integrity Rating
Verify if the Integrity Rating of a component is or is not one of the following:
Normal
Suspicious
Malicious
Other Conditions
The following conditions are related to the other policy type.
Label
Verify if a specific component label is or is not assigned to a component.
Match State
Verify if the comparison of a component to known components is or is not a match in one of the following ways: Exact, Similar, or Unknown.
Format
Verify if the component is in a specified format.
Supported formats include:
a-name, cargo, cocoapods, composer, conan, conda, cran, gem, golang, hf-model, maven, npm, nuget, pecoff, pub, pypi, rpm, swid and swift.
Coordinates
Verify if a component matches the coordinates in the drop down. These include:
a-name, cargo, cocoapods, composer, conan, hf-model, maven, npm, pecoff.
Additional component coordinates introduced in release 189 include:
conda, cran, gem, golang, nuget, pub, PypI, RPM, SWID and swift.
Enter the specific attributes for each type of coordinate. You can use a wildcard (*) at the end of an attribute to broaden the search. The list below describes each component coordinate.
a-Name: a-Name is short for Authoritative Name, an identifier created by Sonatype to identify components agnostic of the repository format. You fill in a name, qualifier, and version.
For example:
Name: log4net Qualifier: Framework 3.5 Version: 2.0.5 Name: log4net Qualifier: Version: 1.*
Cargo: The Cargo component coordinates. You fill in name and version.
For example:
Name: grin Version: 1.1.0
CocoaPods: The CocoaPods component coordinates. You fill in name and version.
For example:
Name: libpng Version: 1.4.9
Composer: The Composer package format. You fill in the name, namespace and version.
For example:
Name: jqueryui Namespace: components Version: 1.11.4
Conan: The Conan component coordinates. You fill in name, version, channel (optional), and owner (optional).
For example:
Name: libxml2 Version: 2.9.8 Owner: bincrafters Channel:
Conda: The Conda component coordinates. You fill in name, version, channel (optional), build(optional), subdir (optional), type (optional).
For example:
Name: numpy Version: 1.21.0 Channel: conda-forge Build: py39_0 Subdir:linux-64 Type: tar.bz2
Cran: The Cran component coordinates. You fill in name, version and type (optional).
For example:
Name: ggplot2 Version:3.4.0 Type: tar.gz
Gem: The Gem component coordinates. You fill in the name, version and platform (optional).
For example:
Name: ggplot2 Version:3.4.0 Platform: linux
Golang: The Golang component coordinates. You fill in the name (module-name) and version.
For example:
Name: github.com/user/project Version:3.4.0
hf-model: The Hugging Face repository model format. You fill in the repository id, model name, version, model format and extension.
For example:
Repo ID: hauson-fan/RagRetriever Model: pytorch_model Version: 4404c42d94447ab738eda599e4632b42a4c47a80 Extension: bin Model Format: pytorch
Maven: You fill in a component’s GAVEC, i.e. Group ID, Artifact ID, Version, Extension, and a Classifier.
For example:
Group ID: org.sonatype.nexus Artifact ID: nexus-indexer Version: 1.0 Extension: jar Classifier: sources Group ID: org.sonatype* Artifact ID: nexus-indexer Version: 1.* Extension: * Classifier:
npm: The npm component coordinates. You fill in the packageId and version.
For example:
PackageId: ramda Version: *
Nuget: The Nuget component coordinates. You fill in the packageId and version.
For example:
PackageId: Newtonsoft.Json Version: 13.0.1
Pecoff: The PECOFF component coordinates. You fill in the name, version and namespace (optional).
For example:
Name: System.IO Version: 1.0.0 Namespace: Microsoft
Pub: The pub component coordinates. You fill in the name and version.
For example:
Name: http Version: 0.15.0
PyPI: The Python component coordinates. You fill in the name, version, qualifier(optional), and extension(optional).
For example:
Name: MarkupSafe Version: 1.1.0 Qualifier: Extension: *
RPM: The RedHat Package Manager (rpm) component coordinates. You fill in the name, version, and architecture.
For example:
Name: bash Version: 5.1.8 Architecture: x86_64
Swid: The SWID component coordinates. You fill in the name, version, tag ID, namespace(optional), tag version (optional), tag creator name (optional), tag creator reg ID(optional), patch(optional).
For example:
Name: ExampleSoftware Version: 1.0.0 Tag ID: exampleTag123 Namespace: com.example Tag version: 1.0 Tag creator name: ExampleCorp Tag creator reg ID: regid.2025-03.com.example Patch:
Swift: The Swift component coordinates. You fill in the name and version.
For example:
Name: MyLibrary Version: 1.0.0
Package URL
Verify if a component matches or does not match a specified package URL. You can use a wildcard (*) at the end of an optional attribute to broaden the search. The package URL must have the format below:
pkg:type/namespace/name@version?qualifiers
type : the package "type" or package "protocol" such as maven, npm, etc. Required
namespace : some name prefix such as a Maven groupid (optional and type-specific). Optional
name : name of the package. Required
version : version of the package. Optional
qualifiers : extra qualifying data for a package such as type, classifier for maven (optional and type-specific). Optional
Maven :
pkg:maven/tomcat/tomcat-util@5.5.23?type=jar
A-name:
pkg:a-name/startbootstrap-agency@4.0.0-beta
Proprietary
Verify if a component is or is not considered proprietary.
Identification Source
Verify if the identification of a component is or is not one of the following:
Sonatype - When the identification is done based on IQ Server data sources
Manual - When the identification is done based on a component claimed by you
Clair - When the identification is done based on a Clair scan result
Package Manifest - When the identification is done based on any manifest file scan
Sonatype-Container - When the identification is done through Sonatype Container scanning
Component Category
Verify if the component category is or is not a specified category. These categories are what the component is used for, as categorized by Sonatype. Possible values include designations like "Data Protocols," "Logging," "Networking Utilities," etc. If a parent category is selected, a match will occur on any child category as well.
Data Source
Verify whether the data source where the component information was found has support for one of the following features: Identityor License
Dependency Type
Verify if the dependency type is or is not the following:
Direct - When the dependency is determined to be defined in the application/project
Transitive - When the dependency is brought in from another dependency
InnerSource - When a direct dependency is determined as an internally developed module. Note that this will not match transitive components that are brought in by InnerSource components.
For more information see the dependency type section in Reviewing a Report
NOTE: Policy is not evaluated on components with a dependency type of unknown. This policy condition does not apply to Repository Firewall.
End of Life (EOL)
Verify if the component has been marked as End of Life (EOL). A policy violation will occur if an EOL component is found during evaluation.
Note
The EOL constraint is currently supported for components of Maven, npm, NuGet, and PyPI format/ecosystems.
For more information on EOL components in your applications, refer to the Component EOL dashboard under Data Insights.
Derivative AI Model
Check if the AI model used in the application is a Derivative AI Model. A policy violation will occur if a derivative AI model is detected during evaluation. The policy violation condition will show the name of the foundational model that the evaluated model is derived from.
For more information on Derivative AI Model, refer to Threats in AI/ML Models.
AI Content
Check if an AI model contains objectionable content. A policy violation will occur if the objectionable AI model is detected during evaluation.
For more information on Objectionable AI Models, refer to Threats in AI/ML Models.
KEV Status
Verify if a component is implicated in a vulnerability listed in the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog published by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). You can create a policy constraint for the following conditions:
Select the Known to be Exploited option from the dropdown to create a policy that triggers an action when a scan detects a component/vulnerability that is listed in the KEV catalog.
Select the Not Listed option from the dropdown to create a policy that triggers an action when a scan detects a component/vulnerability that is not listed in the KEV catalog.
EPSS Score (Percentage)
Evaluate vulnerabilities based on their likelihood of being exploited in the next 30 days as determined by data from the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS). This condition is especially useful for prioritizing vulnerabilities based on actual exploitation risk, independent of their CVSS score.
It functions similarly to other percentage-based conditions, such as Relative Popularity. To configure an EPSS-based policy constraint, you must select the following:
The EPSS Score (percentage) metric.
A comparison operator (=, >, >=, <, <=) to define the threshold logic.
A numeric value (between 0 and 100) representing the EPSS percentage score.
The following table shows how EPSS and CVSS scores together can help estimate actual exploitation risk:
EPSS Score | CVSS Score | Priority |
|---|---|---|
Low | Low | Low, exploitation unlikely |
Low | High | High impact, but exploitation unlikely |
High (> 0.5) | Moderate or High | Critical, exploitation most likely |