Understanding the Shai-Hulud npm Worm Attack
What happened, why it matters, and how Sonatype protects you from npm and Shai-hulud attacks
Recent software supply chain attacks, such as the Chalk/Debug campaign (Sonatype ID: sonatype-2025-003716), the S1ngularity event (Sonatype ID: sonatype-2025-003584), and the Shai-Hulud campaign (Sonatype ID: sonatype-2025-003810), have seen threat actors compromise developer accounts to publish malicious versions of popular npm packages. These attacks are sophisticated, with payloads designed to steal credentials, exfiltrate sensitive data, and even self-propagate like a worm; an incredibly dangerous adaptation for malware.
This escalation in attack sophistication underscores the critical importance of a proactive defense. Sonatype Repository Firewall provides real-time, preventative protection by automatically blocking these malicious components before they can be downloaded into your environment. When a malicious component is identified, Firewall quarantines it, ensuring your builds and development pipelines remain secure. For more detailed information, please refer to our blog posts on the Chalk and Debug package attacks and the ongoing npm software supply chain attacks.
What to do if your files have been compromised
Prerequisite: Sonatype Nexus Repository Version
To take advantage of the remediation steps outlined below, customers must be on Nexus Repository version 3.73.0 or higher. This is the minimum version that includes the Malware Banner feature, which provides a visual indicator and a list of identified malicious components in your repositories. The remediation steps, including the automated tasks, depend on this core feature to function correctly.
If a malicious component was downloaded before Repository Firewall was properly configured, you can use the following steps to find and remove it:
Using Nexus Repository:
Check for the Malware Banner on your NexusRepository dashboard (Version 3.73.0 or higher), which indicates that a malicious component has been identified. Download a CSV list of components from the Malware Banner.
To remove the malicious components, run the Automatic Malware Management task on the affected proxy repositories (Version 3.77.0 or higher). This task, when enabled with Enable Malware Cleanup, will automatically delete the malicious components from your repository. For details, refer to the Automatic Malware Management task documentation.
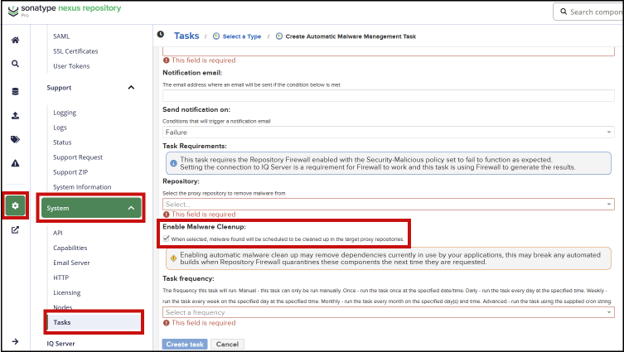
Automatic Malware Management
Using IQ Server:
Utilize Advanced Search in IQ Server to find any violations related to these specific attacks. Use the following search criteria:
vulnerabilityId:sonatype-2025-003584 OR vulnerabilityId:sonatype-2025-003716 OR vulnerabilityId:sonatype-2025-003810
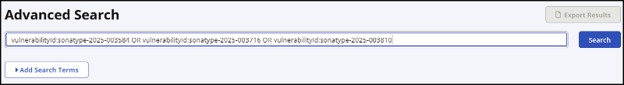
Advanced Search
Use Advanced Search to look for these malware components within your application scans that would indicate the malware entered your CI pipelines via alternative means. If so, you should follow your internal incident response policy and contact your CSE for guidance.
For a comprehensive guide on the manual process of removing malware and handling the malware banner, please consult the Guide to Removing Malware.
Check now that your deployments of Nexus Repository and Repository Firewall were/are correctly configured to block malware
Open Repository Firewall and:
Confirm that all proxy repositories for the npm ecosystem have Audit and Quarantine enabled. Sort the list by Format to quickly identify npm proxy repositories.
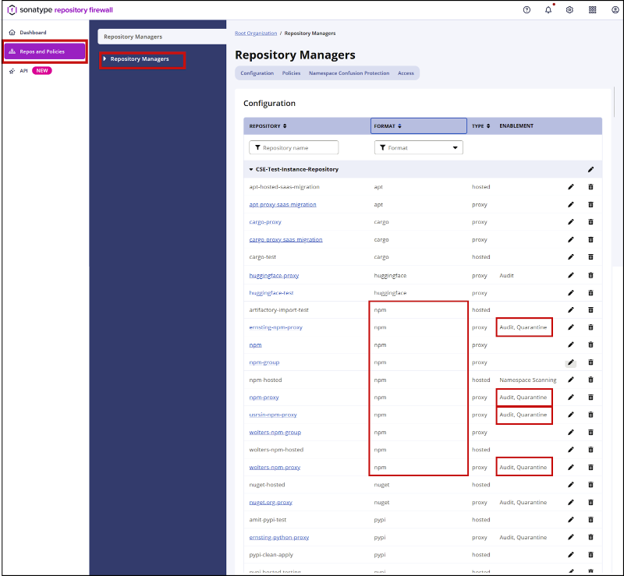
Repository Manager view in Repository Firewall
Read more: Audit and Quarantine documentation
Confirm that your Integrity-Rating and Security-Malicious policies are configured correctly. Make sure they match these screenshots exactly, including the Policy Name field.
Integrity-Rating:
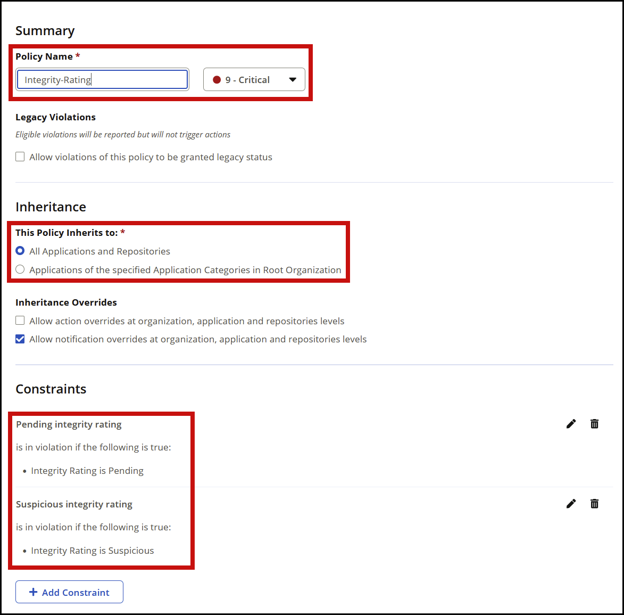
Integrity-Rating
To understand the protection provided by the Release Integrity policy please see our Release Integrity documentation. Policy Compliant Component Selection should also be considered in conjunction with this policy to minimize impact from the latest suspicious packages.
Security-Malicious:
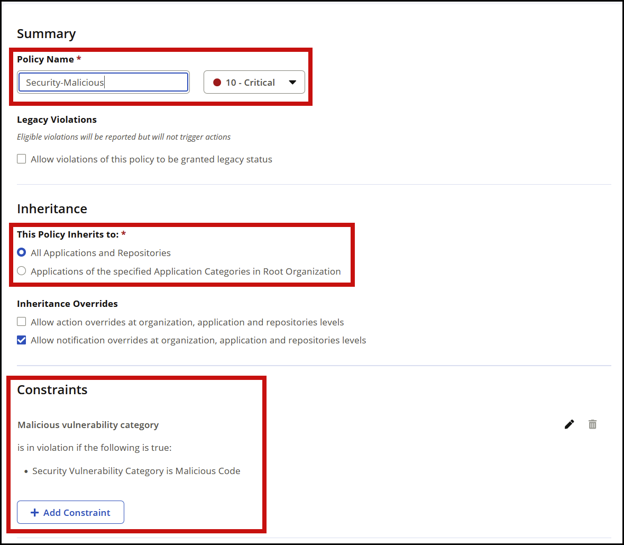
Security-Malicious
Confirm that these policies are set to "Fail" at the proxy stage.
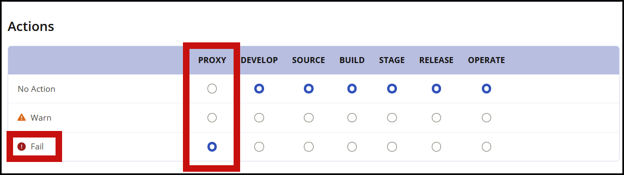
Fail at Proxy Stage
Read More: Release Integrity documentation
If all of these things are confirmed, congratulations: You're protected against these npm malware attacks and the 100,000+ other malicious packages Sonatype has cataloged! Sonatype identified and blocked the malicious chalk and debug npm packages within just two minutes of their publication, showcasing the unmatched speed and protection you gain with our solutions.
Next Steps
Malware attacks are more frequent, more sophisticated, and more dangerous than ever. Maximize your protection against future malware attacks by doing the following:
Review the Integrity-Rating and Security-Malicious policies on a regular cadence and ensure they're set to "Fail" at the Proxy stage. If you're also a Sonatype Lifecycle customer, it's wise to set them to "Fail" at every stage. Remember – there's never a legitimate reason for malware to be in your development ecosystem.
Eliminate development disruption caused by the Integrity-Rating policy by also configuring Policy Compliant Component Selection.
Create a new Audit and Quarantine capability, and be sure it's enabled for every new proxy repository.
Enable Automatic Quarantine Release so that components are released from quarantine automatically if new data confirms they're safe. This avoids developer friction and minimizes "false positives."
If you're a Sonatype Lifecycle or Sonatype SBOM Manager customer, turn on Continuous Monitoring. This will alert stakeholders if malware appears in your apps unexpectedly.
Educate developers on the importance of routing component requests through Nexus Repository. All requests for open-source components, regardless of ecosystem or package manager, should go through Nexus Repository.
For additional protection, integrate Repository Firewall with Zscaler to block downloads of known malware even when developers bypass Nexus Repository.
Additional Resources
Malware vs. Vulnerabilities eLearning
Webinar with CTO Brian Fox and Field Chief Technology Officer Ilkka Turunen