Verify and Repair Data Consistency Tasks
These tasks restore missing data when an artifact that exist in storage is not in the database. This state may happen during the recovery process when failing over into another region or when restoring a database backup that was finalized at a different time then the storage.
Configure the task to reconcile blobs created in the last specified number of days; reducing your recovery time.
Recover lost metadata when restoring Nexus Repository from a backup where the database and a blob store are out of sync.
Tasks Renamed in Release 3.84.0
The tasks have been renamed in the Nexus Repository 3.84.0 release in the user interface to the following:
Repair - Data Repair Plan Repair - Execute Data Repair Plan
These tasks replace the Reconcile Component Database From Blob Store task for all recovery scenarios. The new tasks are faster and more performant while allowing administrators to target a time range while selecting the blob stores and repositories to prioritize the first. Any tasks configured to use the old reconcile task are removing when upgrading to the Nexus Repository 3.83.0 release or later.
Instructions for Use
Running these tasks may take a significant amount of time; impacting recovery timing. Recovery requires using both tasks; the first to generate recovery plans, followed by the second to execute the generated plans. The API may be used to configure the plans, execute the plans, and audit the results.
Step 1: Configure the Data Repair Plan task
Use the scoping properties to limit the amount of time the task takes to repair the prioritized repositories. This is useful when recovering deleted artifacts.
Select the target blobstores. Each selected blobstore is analyzed one at at time. Selecting multiple blobstores will increase the time to recover.
Prioritize specific repositories. All repositories from the blobstore are verified however you may prioritize specific repositories when repairing very large blobstores. This makes artifacts from those repositories available sooner than artifacts from repositories in no particular order.
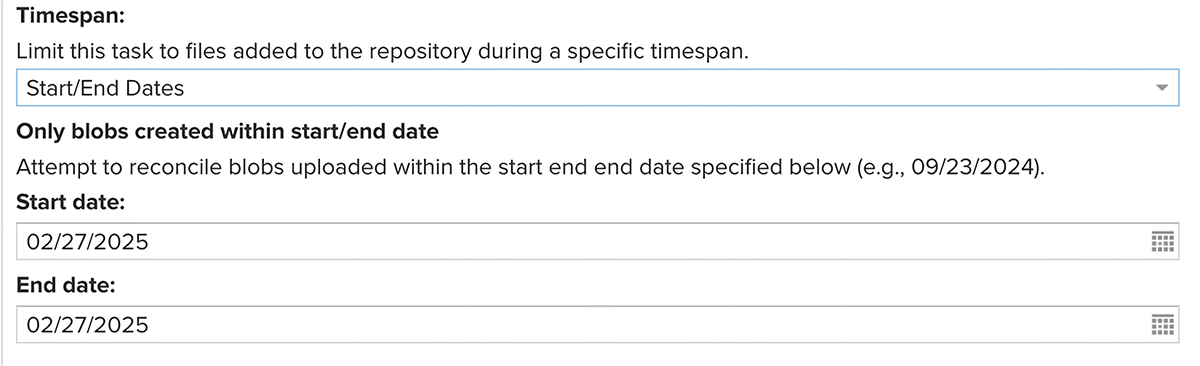
Set the timespan to verify and repair. Include a limit on how far back the task looks for missing components based on the time they were added to the repository. This greatly speeds up the time needed to run the task. Set it to the just before the time of the last backup or when the artifacts had been soft deleted.
Manually run the task. This task must be run manually by the administrator in the UI or using the API to configure and run it.
Running the task creates a plan set to the
PLANNEDstate. The plan is put into theEXECUTEDstate when finished.Use the API to view the plan results. Running the task creates a recovery and results plan to review using the REST API to fetch the specific plan. Results are include in the logs for the task.
Data Repair Plan Task Configuration
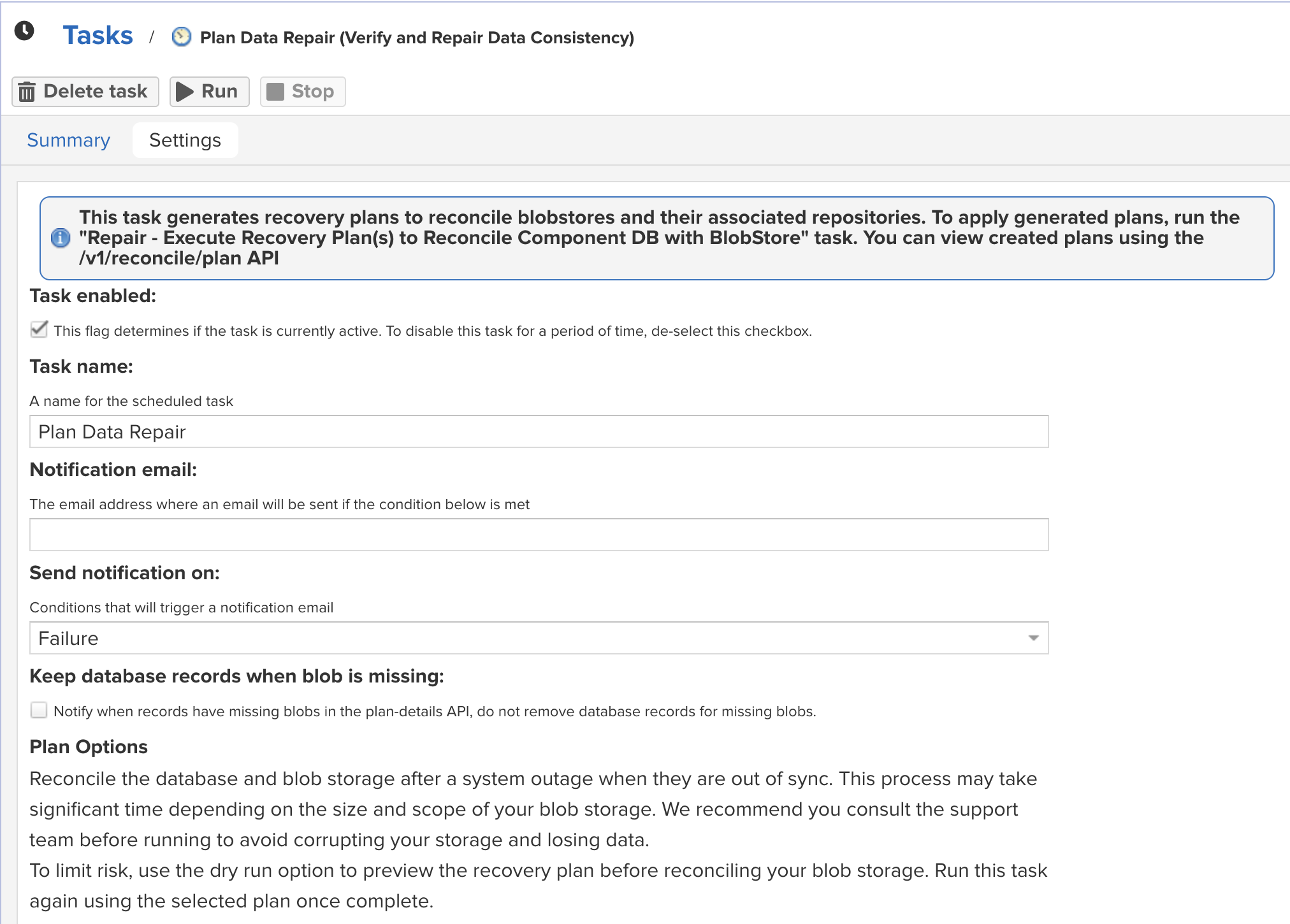
Use previously created plans This option is available when plans have been previously generated from a dry run of the task. Save time by avoiding generating a new plan.
Blob Store Select which blob stores and their order to repair.
Repository Select the repositories and their order to prioritize for repair. All repositories from the selected blob stores are repaired.
Timespan The timing may be limited to a specific duration of time in days, hours, and minutes or by using a specified Start/End Date.

Step 2: Configure the Execute Date Repair Plan task
The summary of the previously ran plans are displayed in the task UI.

Review the previously ran plans. For details of each plan, use the API to fetch a json file of the actions to perform.
Manually run the task. Running the task puts the plans into the
EXECUTEDstate when finished.Use the API to view the execution results. Review the results of the plan execution with the API.
As backups of the database and the storage occur at different times, they may not be consistent with one another during a recovery event. This task compares the available artifact data to reconcile the available differences in the various possible scenarios between this data.
Three steps are performed when artifacts are added to Nexus Repository: (1) the artifacts binary file is saved to storage, (2) a metadata file about the artifact is stored in the same directory with the binary, and (3) an entry about the artifact is stored in the database. This task resolves the differences between these three data sources.
DB (Database) Row The artifact's metadata may exists in the database or is missing. This may happen when the artifacts was added after the database backup was complete or when the artifact was restored from a backup after being deleted.
Metadata The metadata file contains similar data to that which is stored in the database. It contains static information on the artifact binary regardless of where and how it is stored. When soft deleting artifacts, the metadata file and database are updated to indicate that the artifact is to be deleted.
Binary Artifacts are renamed to match their file hash when stored with some metadata retained on the file itself. When the file is found in storage either the database or metadata files may be used to automatically restore the artifact however when they are not present the reconcile may only report the missing files and repair the database/metadata.
The following table lists the recovery scenarios covered by this task. The numbered scenarios represent the recovery steps performed for every artifact when information is present or missing in the database, component metadata file, and the binary file in storage. These actions are how Nexus Repository resolves the scenario with the available data.
Use the API to view the plan-details for the notify action.
Scenario | DB Row | Metadata | Binary | Default Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Exists | Exists | Exists | No Action |
2 | Exists | Exists | Missing | Report missing binary |
3 | Exists | Missing | Exists | Create properties file |
4 | Exists | Missing | Missing | Report missing binary |
5 | Missing | Exists | Exists | Create missing row |
6 | Missing | Exists | Missing | Report missing binary |
7 | Missing | Missing | Missing | No Action |
8a | Exists | Soft Delete | Exists | Remove soft delete flag |
8b | Exists | Soft Delete | Exists * | Notify |
9 | Missing | Soft Delete | Exists | Notify |
10 | Missing | Missing | Exists | Notify |
* In scenario 8a, the artifact hash in database matches the metadata, while in scenario 8b the hash on the artifact differs from the database.
Supported Formats
This task recovers metadata for:
Apt, Docker, Go, Helm, Maven, npm, NuGet, p2, PyPI, R, Raw, RubyGems, Yum
API Reference
The tasks may be configured and run using the following Reconcile Plan API endpoints. See the Swagger interface for the required properties and configuration.
GET /v1/plan Get list of currently available plans
POST /v1/plan Create reconciliation plans with selected parameters
PUT /v1/plan Execute all non executed reconciliation plans
GET /v1/plan/{planId} Delete all non executed reconciliation plans
GET /v1/plan/{planId} Get single reconciliation plan with details
PUT /v1/plan/{planId} Execute a reconciliation plan based on its Id
DELETE /v1/plan/{planId} Delete a reconciliation plan based on its Id
GET /v1/plan/details Get reconciliation plan details
Performance Considerations
To speed the recovery of blobs, a new date-based blob store layout was introduced in the 3.83.0 release of Nexus Repository. Prior to this change, blobstores used a vol/chap layout which did not organise the blobs by date. While the new layout is used for blobs added to the repository after upgrading to versions after the 3.83.0 release, blobs that pre-date the upgrade remain in the previous layout.
When the task is run with a timespan to include blobs that predates the upgrade to a version after the 3.83.0 release, the task may take significantly longer to complete as the task must iterate over every blob using the previous layout and check its modification timestamp.
Performance Testing
In terms of functional validation, in all tests executed, there were more than 99.9% of records created in the DB based on the blob files. The 100% is typically not reachable in all cases, as we're triggering a failure and there are a small number of missing records. Some tests reached 100% of the records recovery.
The formats used to test were raw and maven, while the results vary depending on the format, the general pattern of the task execution is similar for all of them.
While the system is back working in less than 20 minutes, the reconciliation task can take further time depending on the number of records missing.
In the Maven case, restoring more than 129K files may take more than 3 hours with a thread pool of 2.
It can take between 13 and 51 milliseconds to restore each row missing from the blob files, this figure mainly depends on the thread pool size parameter. With the parameter set to 8, the time taken for raw assets to be restored can be 3X shorter than when having the parameter set to 2. The format to reconcile has to do with the performance of the task