High Availability Deployment Options
Only available in Sonatype Nexus Repository Pro. Interested in a free trial? Start here.
What is High Availability?
High Availability (HA) refers to increased uptime accomplished by deploying a cluster of redundant Nexus Repository instances in active/active mode (i.e., both actively running simultaneously) within a single cloud region or on-premises data center. This allows you to maintain Nexus Repository availability even if an instance becomes unavailable.
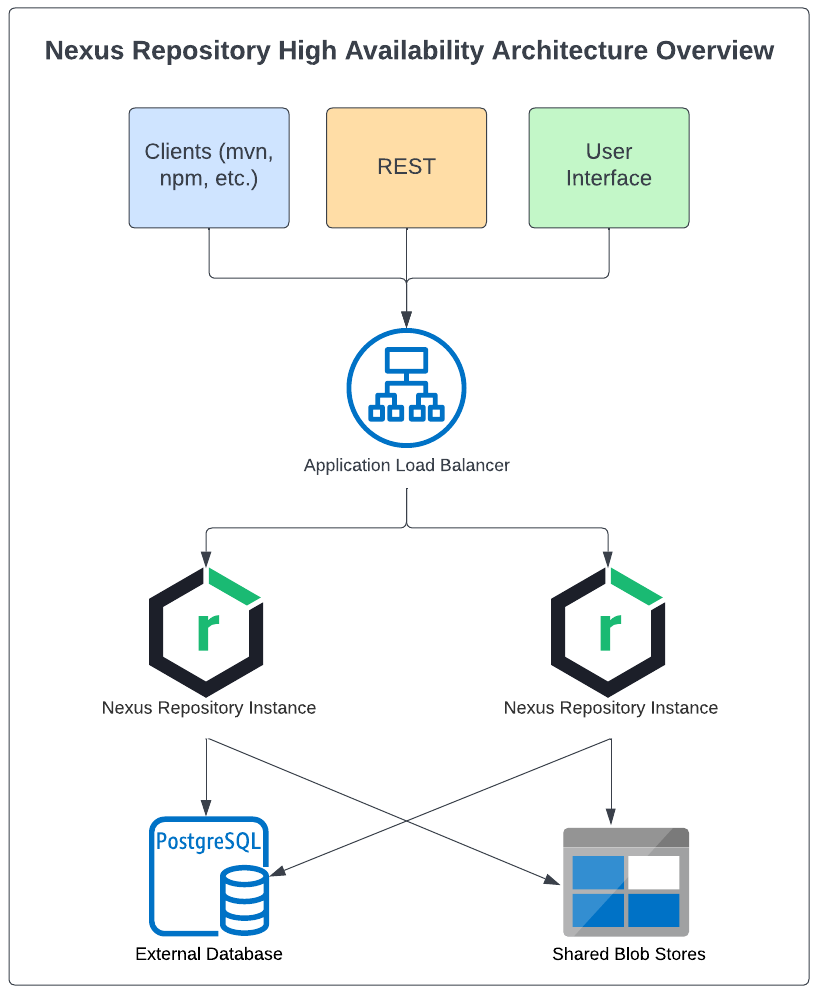 |
Use Cases
HA is designed to protect against the following scenarios:
An Availability Zone (AZ) outage within a single region
A virtual machine/bare metal/EC2 instance failure
A Nexus Repository instance failure
As such, HA is an appropriate solution for mission-critical Nexus Repository deployments that require continuous operations or uptime for an extended period and can help such instances scale for load.
It also provides the following necessary functionality to highly scalable Nexus Repository deployments that must meet varying loads:
Manually scale repository instances
Auto scale instances in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Deploy in Kubernetes to facilitate scaling instances up and down without having to shut down Nexus Repository
Note
Note that HA requires additional infrastructure and maintenance overhead. Deploying HA without a strong need or use case may not yield your desired return on investment.
Choosing High Availability
HA is an advanced feature that requires careful consideration. Consider the following points before deploying to an HA environment:
Containerized and cloud HA deployments require using several advanced technologies (e.g., Kubernetes, cloud technologies) outside the Sonatype Suite's scope. You should ensure that you have in-house expertise in these technologies before attempting an HA deployment.
HA requires additional infrastructure and maintenance overhead (See Sonatype Nexus Repository High Availability Performance Data (AWS, Azure)). Deploying HA without a strong need or use case may not yield your desired return on investment.
Sonatype Nexus Repository High Availability deployments should be fully deployed and tested in a development environment before attempting to deploy in production. Improper deployment in a production environment can result in critical data loss.
Search Feature Differences in an HA Environment
The search feature implemented for high availability (HA) differs a great deal from the search currently used in a non-HA environment.
HA search has the following requirements:
At least one search criterion is required when searching through the UI
At least one additional search criterion is required beyond format when searching through the UI
Each search criteria must be at least three characters long
Leading wildcard search is not supported; however, you may use a trailing wildcard (i.e., prefix search)
Searches cannot begin with special characters followed by a wildcard
All keyword searches automatically append a wildcard (*) at the end of each criterion
Example Invalid Search Patterns
The following search patterns are some that may work in non-HA environments but will not work in an HA environment
Invalid Pattern | Reasoning |
|---|---|
"*" | Less than three characters long; leading wildcard not supported |
"he*" | Less than three characters long |
"he*@_" | User criteria ("@_") contains only an underscore |
"he*@/" | User criteria ("@/") contains only a forward slash |
"he*@*" | User criteria ("@*") contains only a wildcard |
"/*/hel" | Search begins with a special character followed by a wildcard |
"$%*hel" | Search begins with two special characters followed by a wildcard |
Refetch Limits and Search Configuration Capability
As of 3.72.0, Nexus Repository will only make 10 trips to the database to return a result set in a PostgreSQL HA deployment. You can adjust this limit by creating a Search Configuration Capability specifying a different refetch limit. Setting the refetch limit to "-1" will allow unlimited database queries; however, this can result in slower performance in very large deployments. In some scenarios, the refetch limit may result in missing or empty search results.
You must have clustering enabled to see the Search Configuration capability option.
Logging
Container-based cloud deployments use statefulsets to dynamically provision a volume per pod. This is done through dynamic provisioning of EBS for AWS, Azure Disk for Azure, or Cloud Logging for Google Cloud.
For both container and non-container-based on-premises as well as for non-container-based cloud deployments, each Nexus Repository instance runs on a single VM/bare metal machine and will write logs to the local disk.
In all cases, the correct node will respond to support zip generation requests and store the generated zip in the blob store.
Note
The Log Viewer is not available when using an HA deployment options.
Blob Storage
Enabling HA will disable the ability to create default blob stores and repositories. If you are already using the default blob store on your instance, you will need to follow the instructions in Migrating to Shared Blob Storage to change your default blob store's path to connect to a shared location.